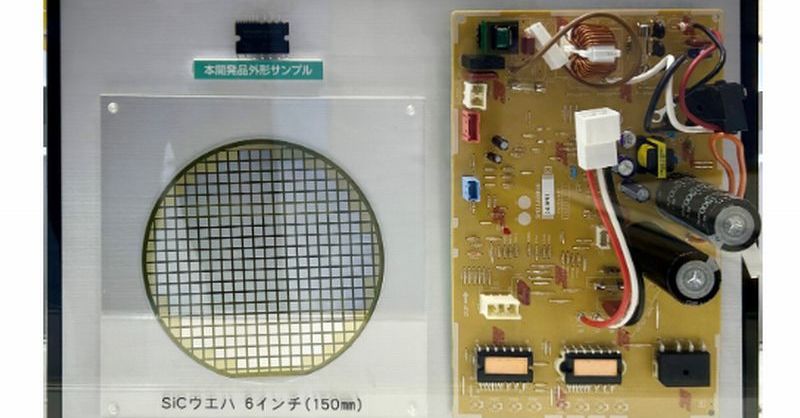
New IPM with SiC: Slashing Aircon Energy Use
Revolutionizing Cooling: Silicon Carbide's Impact on Air Conditioner Efficiency
The global quest for sustainable energy solutions is driving innovation across various sectors, and the air conditioning industry is no exception. Traditional air conditioners are notorious energy guzzlers, contributing significantly to carbon emissions. However, a groundbreaking development promises to dramatically change this: the integration of Silicon Carbide (SiC) technology with Intelligent Power Modules (IPMs). This new approach is poised to slash energy consumption in air conditioners, offering a significant step towards a greener future.
What are Intelligent Power Modules (IPMs)?
IPMs are sophisticated power electronic devices that combine several components – including power transistors, gate drivers, and protection circuits – onto a single substrate. This integration improves efficiency, reduces size and weight, and simplifies the overall design of power systems. Think of them as the brains of the air conditioner's power management system.
IPMs: The Heart of Modern Air Conditioning Efficiency
Traditionally, air conditioners relied on IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) based IPMs. While functional, IGBTs have inherent limitations in terms of switching speed and energy losses. This translates to less efficient cooling and higher energy bills.
The SiC Revolution: Higher Efficiency, Lower Emissions
The game-changer lies in the use of Silicon Carbide (SiC) MOSFETs within the IPM. SiC offers superior properties compared to traditional silicon, enabling:
- Higher Switching Frequencies: SiC allows for much faster switching speeds, minimizing energy losses during operation.
- Reduced Power Losses: Lower energy losses directly translate to lower energy consumption and higher efficiency.
- Smaller and Lighter Designs: SiC devices are smaller and lighter, enabling more compact air conditioner designs.
- Improved Reliability and Durability: SiC's robustness contributes to longer lifespan and less frequent maintenance.
How SiC-based IPMs impact Air Conditioner performance:
- Significant Energy Savings: Estimates suggest energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional air conditioners. This translates to substantial cost reductions for consumers and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Enhanced Cooling Capacity: The improved efficiency also means the air conditioner can provide the same or better cooling performance while consuming less energy.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Lower energy consumption directly contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
The Future of Cooling: SiC's Expanding Role
The adoption of SiC-based IPMs in air conditioners is not just a technological advancement; it's a vital step towards a more sustainable future. This innovation is not limited to residential air conditioning; it holds significant potential for commercial and industrial applications, leading to broader energy efficiency improvements across the sector.
Beyond Air Conditioners: Wider Applications for SiC Technology
The benefits of SiC technology extend beyond air conditioning. This material is finding increasing applications in various power electronic devices, including:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): SiC power semiconductors significantly improve the efficiency and range of electric vehicles.
- Solar Inverters: SiC enhances the efficiency of solar power systems, maximizing energy generation from renewable sources.
- Industrial Drives and Motors: SiC technology improves the performance and energy efficiency of industrial machinery.
Conclusion: Embracing a Cooler, Greener Future
The integration of SiC-based IPMs in air conditioners marks a pivotal moment in the quest for energy-efficient cooling solutions. This technology offers substantial benefits to consumers, the environment, and the air conditioning industry as a whole. As the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, we can expect to see significant reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, creating a cooler and greener future for all.
Call to Action: Learn more about the latest advancements in energy-efficient cooling technologies and explore how you can contribute to a sustainable future by visiting [link to relevant resource/organization].