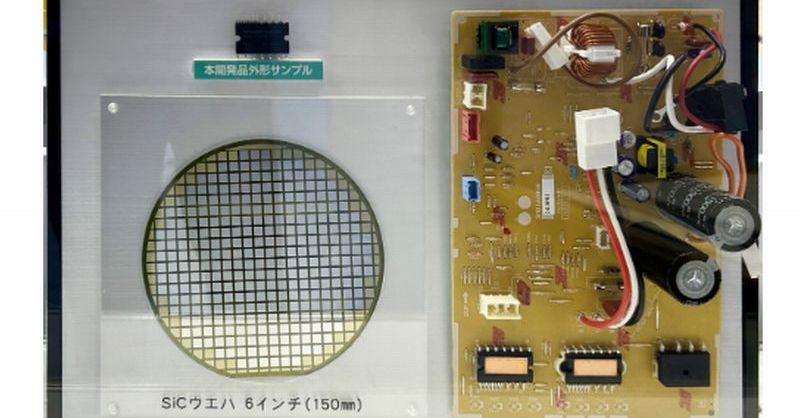
Efficient Air Conditioning: Revolutionizing Cooling with New SiC IPM Development
The air conditioning industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the urgent need for energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. A key player in this revolution is the development of new Silicon Carbide (SiC) Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBT) power modules, promising a significant leap forward in AC efficiency and performance. This article delves into the exciting advancements in SiC IPM technology and its implications for the future of air conditioning.
The Quest for Energy-Efficient Cooling
Global warming and rising energy costs are pushing the demand for more sustainable cooling solutions. Traditional air conditioning systems, often relying on older IGBT technology, suffer from significant energy losses and contribute to a substantial carbon footprint. The search for more efficient alternatives has led to significant investment in research and development, with SiC IPM technology emerging as a frontrunner.
What are SiC IPMs and Why are they Game-Changing?
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a wide-bandgap semiconductor material offering superior performance compared to traditional silicon. SiC IGBTs boast:
- Higher Switching Frequencies: This allows for smaller, lighter, and more efficient power modules.
- Lower Switching Losses: Reduced energy waste translates to significant energy savings and lower operating costs.
- Improved Thermal Management: SiC's inherent properties lead to better heat dissipation, enhancing system reliability and lifespan.
- Increased Power Density: More power can be packed into a smaller space, making them ideal for compact AC units.
These advantages, combined into a single Integrated Power Module (IPM), dramatically enhance the efficiency of air conditioning systems. The IPM integrates all necessary power components, simplifying design and reducing manufacturing complexity.
The Impact on Air Conditioning Systems
The integration of SiC IPMs into air conditioning systems promises several benefits:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Expect significant reductions in electricity usage, translating directly to lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Improved Efficiency Ratings: Higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings become achievable, making these systems more attractive to consumers and policymakers.
- Smaller and Lighter Units: The higher power density allows for the creation of more compact and lightweight AC units, improving design flexibility and installation convenience.
- Enhanced Reliability and Durability: Improved thermal management contributes to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The market for SiC-based power devices is rapidly expanding, driven by increasing demand from various industries including automotive, renewable energy, and now, air conditioning. Several major manufacturers are investing heavily in the development and production of SiC IPMs, ensuring a growing supply to meet the increasing market demand. We can anticipate seeing more widespread adoption of SiC IPM technology in residential and commercial air conditioning systems in the coming years.
Conclusion: A Cooler, Greener Future
The development of advanced SiC IPMs represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future for air conditioning. The benefits extend beyond reduced energy consumption to encompass environmental responsibility and improved technological performance. As this technology matures and becomes more widely available, expect to see a considerable shift towards greener, more efficient cooling solutions for homes and businesses worldwide.
Learn more: For further information on the latest advancements in SiC technology, explore resources from [link to a relevant industry association or research institution]. [Link to another relevant article on your site].
(Note: Replace bracketed links with actual URLs to relevant resources.)