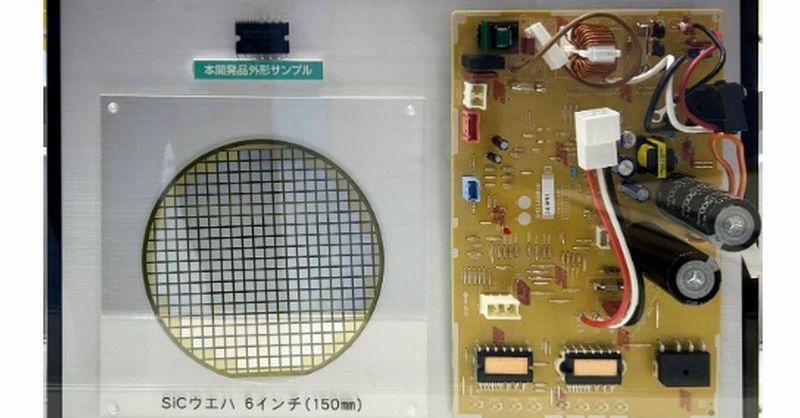
Power Saving AC: Revolutionizing Cooling with SiC-Based IPM Technology
The quest for energy-efficient cooling solutions is constantly evolving, and a significant leap forward has been made with the introduction of SiC-based Intelligent Power Modules (IPMs) in air conditioning systems. This innovative technology promises to drastically reduce energy consumption, leading to substantial cost savings and a smaller carbon footprint. This news article delves into the specifics of this groundbreaking development and its implications for the future of air conditioning.
What are SiC-Based IPMs and How Do They Work?
Traditional air conditioners rely on Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) to control the compressor's power. However, IGBTs suffer from significant power losses, especially at high frequencies. Silicon Carbide (SiC), a wide-bandgap semiconductor, offers a superior alternative. SiC-based IPMs boast significantly lower switching losses and higher operating temperatures compared to IGBT-based systems. This translates directly into:
- Increased Efficiency: SiC IPMs allow for more precise control of the compressor, minimizing energy waste during operation.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Lower energy consumption means lower electricity bills for consumers and a smaller environmental impact.
- Smaller and Lighter Units: The higher efficiency allows for the use of smaller and lighter compressors, potentially leading to more compact AC units.
- Improved Reliability: SiC's inherent robustness contributes to a longer lifespan and enhanced reliability of the AC system.
The Science Behind the Efficiency Gains
The key lies in SiC's superior material properties. Its wider bandgap allows for higher blocking voltages and faster switching speeds compared to silicon. This results in minimal energy loss during the switching process, a major source of inefficiency in conventional AC systems. The higher operating temperature tolerance also contributes to improved performance and durability.
The Environmental Impact of SiC-Based Power Saving AC
The widespread adoption of SiC-based IPM technology in air conditioners holds immense potential for mitigating climate change. The reduction in energy consumption directly translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable future. This makes it a crucial technology in addressing the growing global energy demand and the environmental challenges associated with traditional cooling systems.
A Step Towards Sustainable Cooling
Many organizations and governments are actively promoting energy efficiency initiatives. The development of SiC-based IPMs aligns perfectly with these efforts, offering a practical and effective solution to reduce the environmental impact of air conditioning. This technology could play a pivotal role in achieving global sustainability goals.
The Future of Power Saving AC: What to Expect
While still relatively new, SiC-based IPM technology is rapidly gaining traction within the air conditioning industry. We can expect to see:
- Increased Market Penetration: More manufacturers are likely to incorporate SiC IPMs into their AC units in the coming years.
- Falling Prices: As production scales up, the cost of SiC-based IPMs is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to consumers.
- Further Innovation: Ongoing research and development will continue to improve the efficiency and performance of SiC-based power saving AC units.
Conclusion: A Cooler, Greener Future
SiC-based IPM technology represents a significant advancement in air conditioning technology. By drastically improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact, it paves the way for a cooler and greener future. This innovation highlights the ongoing efforts to develop sustainable and efficient cooling solutions, crucial for addressing the increasing global energy demand and environmental concerns.
Keywords: Power Saving AC, SiC-based IPM, Intelligent Power Modules, Silicon Carbide, Energy Efficiency, Sustainable Cooling, Green Technology, Air Conditioning Technology, Climate Change, Energy Consumption, Compressor Technology.
(Optional CTA): Learn more about the latest advancements in energy-efficient cooling solutions by subscribing to our newsletter!